Hypermobility Syndrome In Children
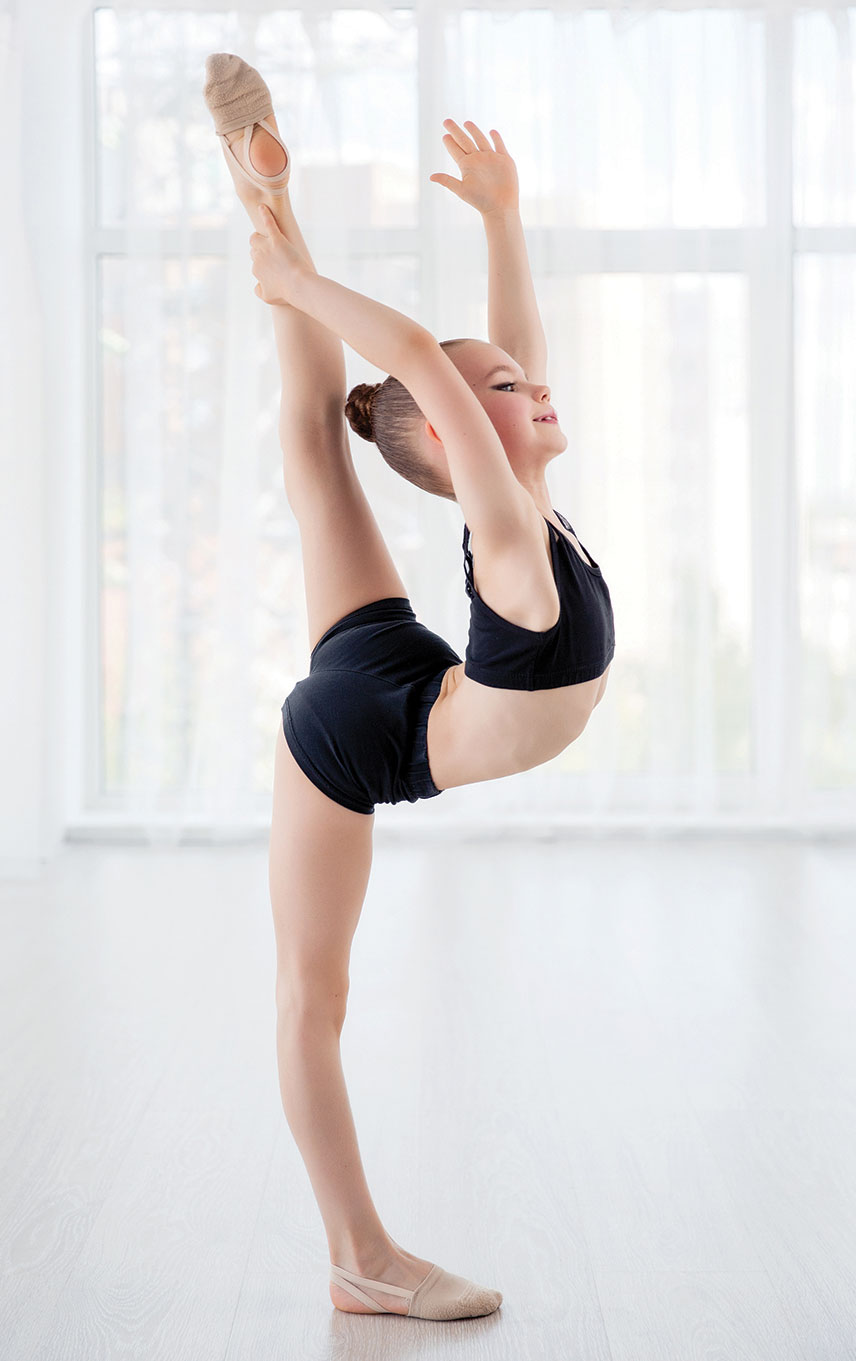
Hypermobility syndrome in children. Flat feet Back pain non-specific Abdominal pains non-specific Chest pains non-specific Fatigue Headaches Tiredness. Many famous gymnasts musicians trapeze artists and dancers have been able to achieve fame due to the flexibility of their joints. This is normally something a child is born with.
The term benign hypermobility joint syndrome BHJS is a common source of joint or muscle complaints that often cause concern for parents children and school personnel. Generalised joint hypermobility is where multiple joints in the body are affected. Generalised joint hypermobility is where multiple joints in the body are affected.
This reason the preferred term to use is Joint Hypermobility Syndrome JHS. Often get tired even after rest. However some children have a condition called Joint Hypermobility Syndrome or JHS.
Hypermobility is thought to be mostly due to genetics. Children who are predisposed to developing hypermobility may do so due to inheriting specific genes from their parents. It affects 7.
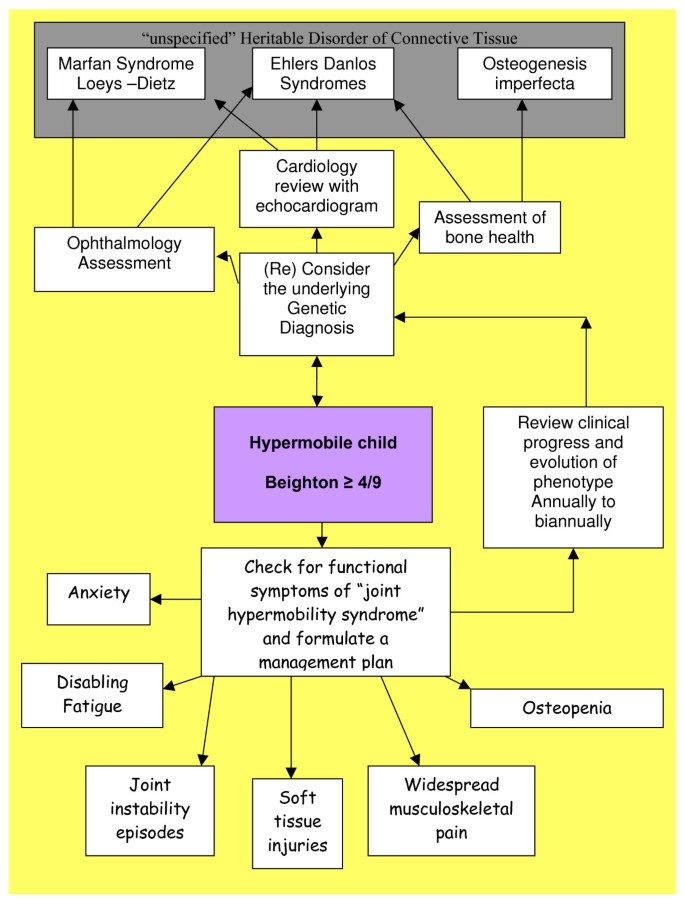
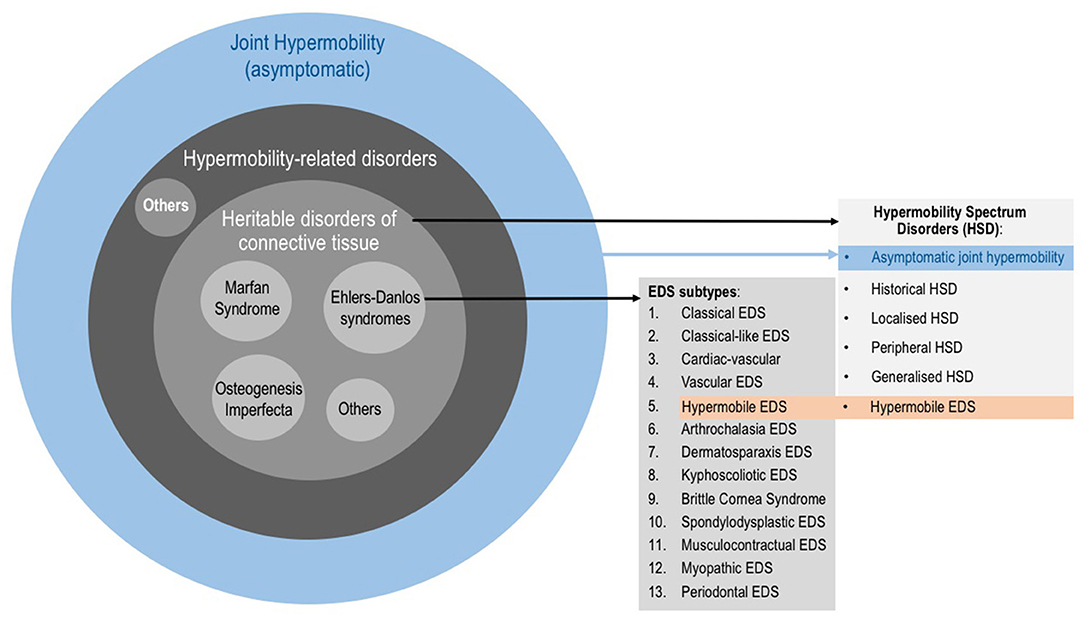
Ligaments are composed of connective tissue which includes collagen fibres. It usually affects children and young people and often gets better as you get older. Hypermobility syndromes is an umbrella term for a number of complex heritable disorders of the connective tissue HDCTs which feature among a diverse constellation of symptoms some hypermobility in some or all of the musculoskeletal system.
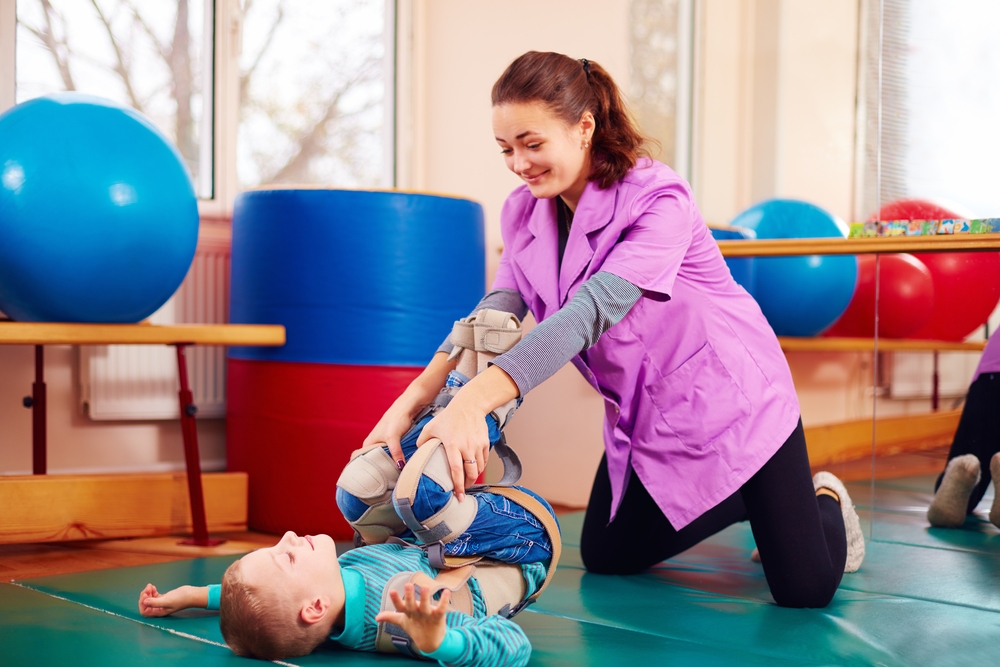
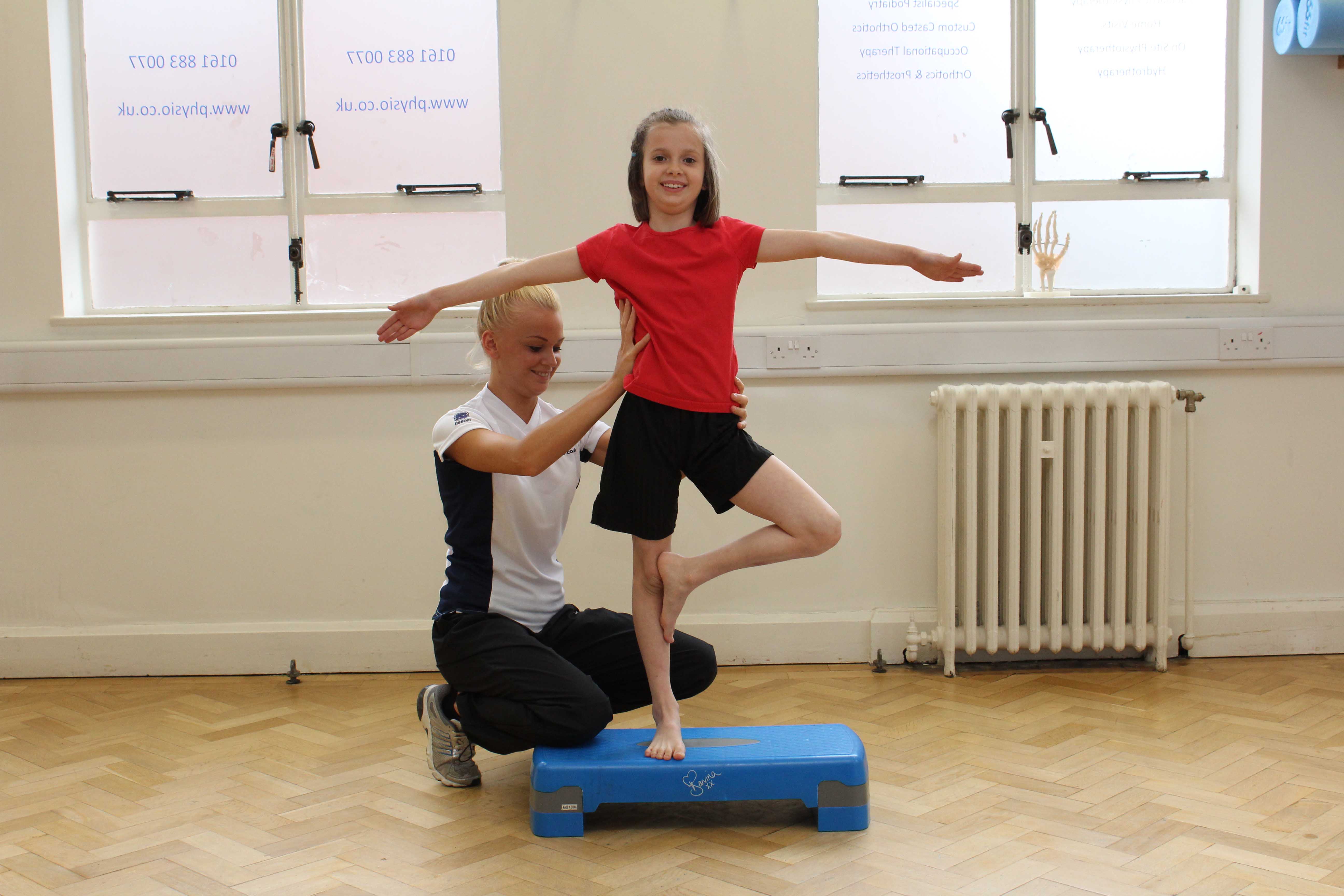
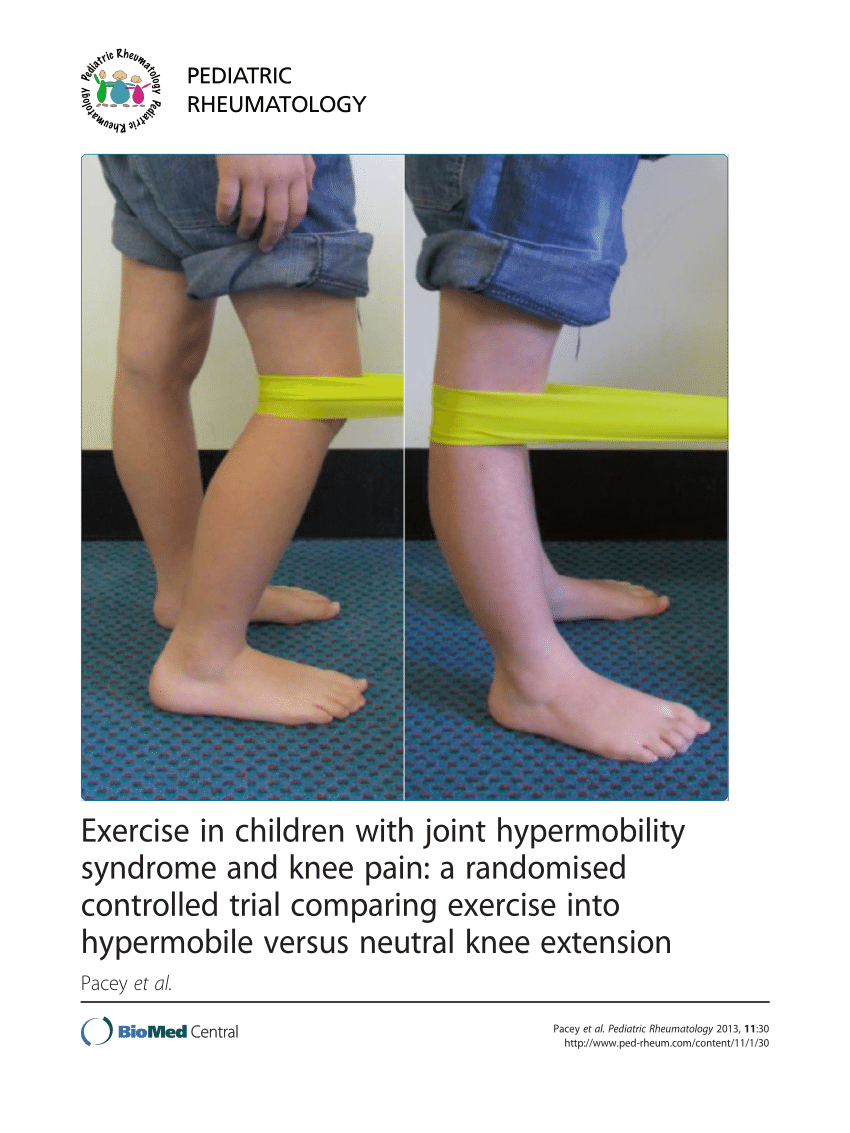
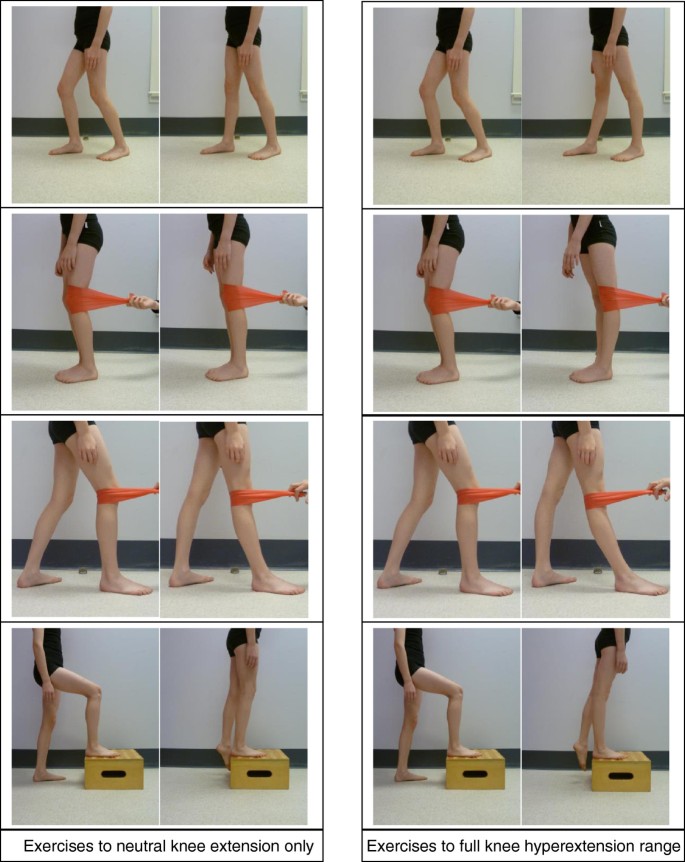
Many children and adults will have one or more double joints. Management in the community for example by a physiotherapist or podiatrist with paediatric expertise is usually appropriate for a child with hypermobility if all of the. Most children and adolescents with flexible joints do not have any adverse symptoms but some individuals may need to take extra care to protect their joints from injury.
Its determined by a number of factors including the pliability of connective tissue the shape of the joints themselves muscle tone and hereditary factors Jane explains. Assessing and managing this condition in children and young people requires specialist knowledge since for all the extra-articular symptoms including abdominal involvement headaches fatigue etc.
Flat feet Back pain non-specific Abdominal pains non-specific Chest pains non-specific Fatigue Headaches Tiredness.
Benign hypermobility describes a child that has several joints that are more flexible than usual. Some children have what doctors call hypermobility spectrum disorder HSD or other conditions which we call Connective Tissue Disorders. For most children hypermobility affects just the joints. Children who are predisposed to developing hypermobility may do so due to inheriting specific genes from their parents. Most of the time hypermobility occurs without an underlying condition and does not necessarily cause any problems. It may also be referred to as ligamentous laxity or joint laxity. This reason the preferred term to use is Joint Hypermobility Syndrome JHS. It usually affects children and young people and often gets better as you get older. It is more common in females than males affecting approximately twice as many females.
Hypermobility is thought to be mostly due to genetics. Excessive motion at the joints. Generalised joint hypermobility is where multiple joints in the body are affected. For most children hypermobility affects just the joints. See a GP if you. Most children and adolescents with flexible joints do not have any adverse symptoms but some individuals may need to take extra care to protect their joints from injury. Joint hypermobility Children and adolescents with joint hypermobility have joints which move beyond the normal limits.







































Posting Komentar untuk "Hypermobility Syndrome In Children"