foot pain in kids
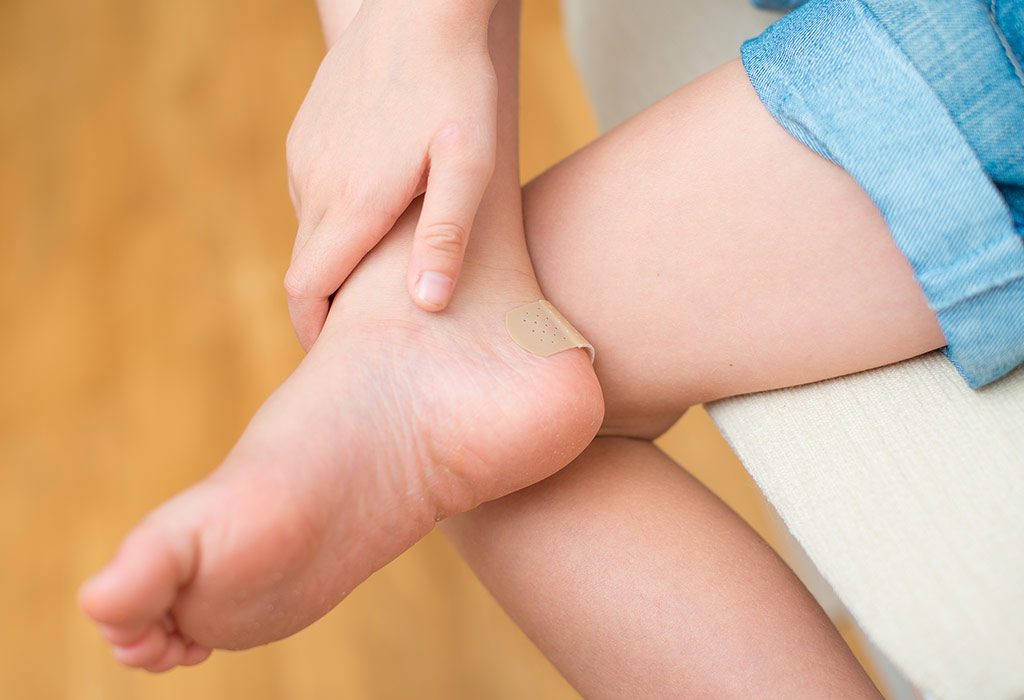 Foot Pain in Kids - Reasons and Home Remedies
Foot Pain in Kids - Reasons and Home RemediesDo not ignore standing problems in children, says the doctor Many children suffer from standing problems that are often not diagnosed. There are many symptoms that parents can see, says Dr. Bradley Lamm, a Baltimore foot and a ankle surgeon and fellow American College of Foot ' Surgeons. Many parents think that children can overcome standing problems, but Lamm said it is important to receive treatment. What are some common pediatric foot conditions? The ankle and foot problems are common in children due to their high levels of physical activity, but it is easy for signs and symptoms of the underlying foot and ankle conditions to get unnoticed because children are so resistant. To support the health of your child's feet, keep an eye out for common ankle symptoms and standing problems and consult with a surgeon standing and ankle if you notice ankles spinning more than usual, flat-foot bow, cramps, pain, limping, or a change in the level of physical activity or the child's desire to play outside. Some conditions are more common than others: •Flatfoot is usually a hereditary condition that occurs when the foot lacks a bow. The flat foot can be painful, and it can usually be treated with orthotics (siders of the ring), along with the stretching of the calf muscle. •Investment disease, commonly known as a "chea oil", is a disturbance of the growth plate that can appear in children who are very active in sports. Symptoms include pain under the lower or rear heel, and possibly limping as the condition gets worse. •The powder occurs at birth and can often be diagnosed before birth with ultrasound. The treatment is usually immediate, approximately a week after birth, with a specialized melting technique during the first two months, and then specific shoes and a bar is used up to 4 years of age. •Toradic coalitions usually occur in older children, usually between 9 and 14 years old. Taral coalitions occur when the rotary joint merges with a "spinal bridge". Symptoms include a stiff foot that can be quite painful, which decreases the activity of the child. •The lesions of the growth plate usually result from the foot or ankle injury, a common occurrence among active young people. Fractures or sprains may damage the growth plate so that it does not grow more bone or the position of the bone is deformed. • Bandits usually occur due to the increased movement of the arch region and present as a blow inside the foot ball. This bone cap is painful, as well as the deviation of the fat finger against the second finger. This bunion deformity is painful with shoes and activity. The surgery of the guided culture plate can correct bunion at an early age (8-13) through a minimal incision. It is better to seek medical advice before, as the treatment will probably be easier and the child would have a greater chance of returning to the activity or sport more quickly. What does the treatment imply for these conditions? Initial treatment options for pediatric pain and foot/ankle injuries include rest, personalized orthosis, and anti-inflammatory drugs. If conservative treatments do not relieve symptoms and conditions persist or worsen, more aggressive treatments may be required, including surgery. Treatment should be determined in consultation with a foot and ankle surgeon, taking into account the age of the child and the progression and severity of the condition. At what age do you begin to see the standing conditions in children? The standing and ankle conditions and injuries can occur to children at any age, but are very likely in very active children. Children who play multiple sports or participate in multiple teams are generally more likely to experience foot and ankle injuries or excessive use conditions. Club teams, in particular, impose on children an increasing demand to play more frequently. In addition, hard play surfaces, including indoor and grass installations, increase demands on feet and ankles. Our practice often sees children from 7 to 18 years of age due to conditions derived from many different sports activities. How is pediatric foot conditions different from adult treatment treated? Fortunately, young patients often feel less pain, heal faster and are more mobile than adults. When surgery is needed, children also have greater healing potential than adults. Other differences include the need to explain the condition thoroughly to both the child and the father. What are the long-term consequences of not treating standing conditions in children? The Morning Sun Bulletin A common misconception I see in patients who previously visited a doctor or pediatrician is that children will grow from standing conditions like the pediatric flat footing, which is simply not true. Many children may have legs in the feet or intestine, which may be normal, but others may be abnormal. A comprehensive assessment by a foot and ankle surgeon is necessary to determine the diagnosis and whether or not it needs treatment, monitoring or anything at all. Long-term consequences of not treating these conditions may include pain, joint arthritis, muscle weakness, overload of the opposite foot and ankle, deformity, inactivity and mental frustration. Who do I see for my son's foot and ankle pain? In the years before the foot and ankle growth plates are fully developed, the lesions of the growth plates in children can be very difficult to treat. The foot and ankle surgeons are specially trained in this area and are used to taking care of the growth plates, bones and soft tissues in the development of children. Latest Health Twitter.com/ankwalker Recommended in Baltimore SunLatest Health
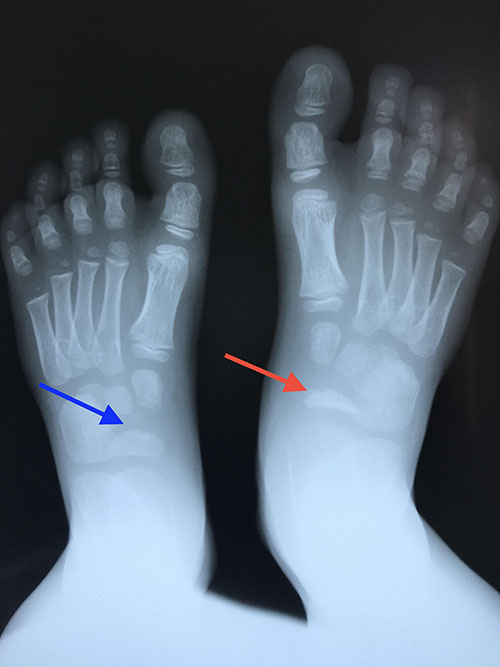
Facts About Arch Pain and Heel Pain in Kids | Healthy Feet Podiatry
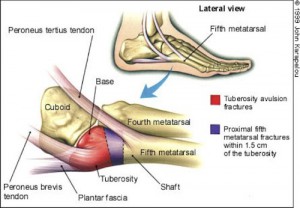
Kids Outer Foot Pain – My FootDr

Common Foot Problems in Children: What to Do and When to Worry | Nagy Footcare
My Child's Feet Always Hurt – What's Going On? | University of Utah Health

5 Signs of Kids' Foot Problems – Shoal Creek Foot & Ankle Center

Does Your Child Complain Of Foot Pain? - Sports And Spinal Group

3 Ways to Treat Foot Pain in Children - wikiHow

Heel Pain in Kids: Causes and Treatments
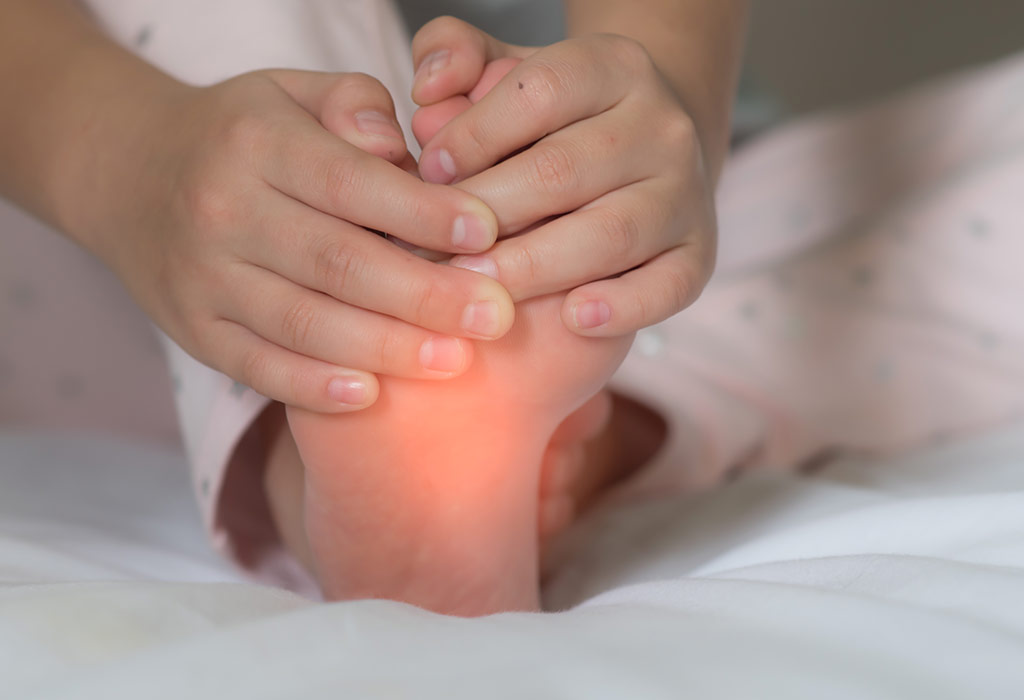
Foot Pain in Kids - Reasons and Home Remedies

Kids Under 7: Children's Foot Problems

Heel Pain in Children | Clifton Foot And Ankle
How to deal with your child's growing pains - Today's Parent

5 warning signs of foot and leg pain in children - OnePoint Podiatry, Penrith

Why Does My Child's Feet Hurt? - Life With Bobux | Bobux

Foot Pain in the Top of the Foot | Stop Your Kids' Foot Pain! | Fitting Children's Shoes

Foot Pain & Leg Pain in Kids & Toddlers | Elite Podiatry
Children's Foot Care | Dr. Alice Wang

Why Kids Get Ingrown Toenails (What to Do About Them) | Fixing Feet PLLC

Children's & Kid's Feet Archives | Page 2 of 2 | Foot Health Clinic Samford Village QLD
Centerpoint Pain Clinic - Kids Feet
/142019675-56a36f8e5f9b58b7d0d1f276.jpg)
Common Pediatric Foot Problems
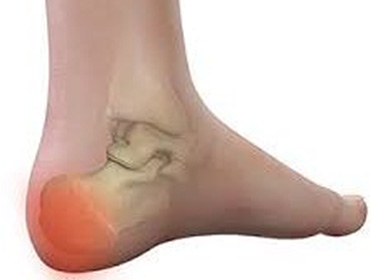
IS HEEL / FOOT PAIN STOPPING YOU PLAYING WITH YOUR KIDS? - barefeetpodiatry

What are 'flat feet' in children and are they something to worry about?

Children's Foot Care Treatment | Foot Doctor Fair Lawn NJ 07410 and Paterson, NJ 07514
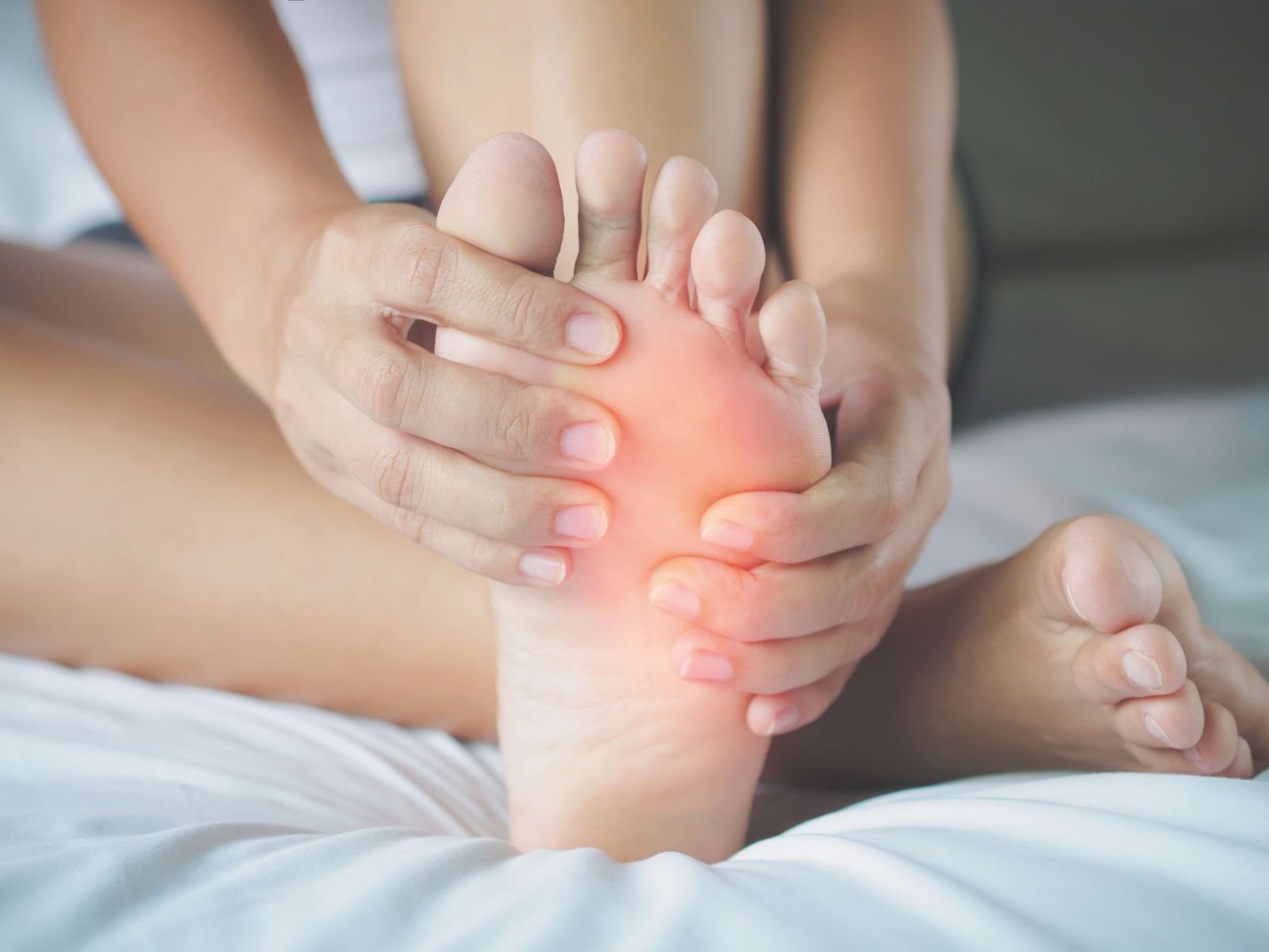

What's causing those swollen feet? - Harvard Health
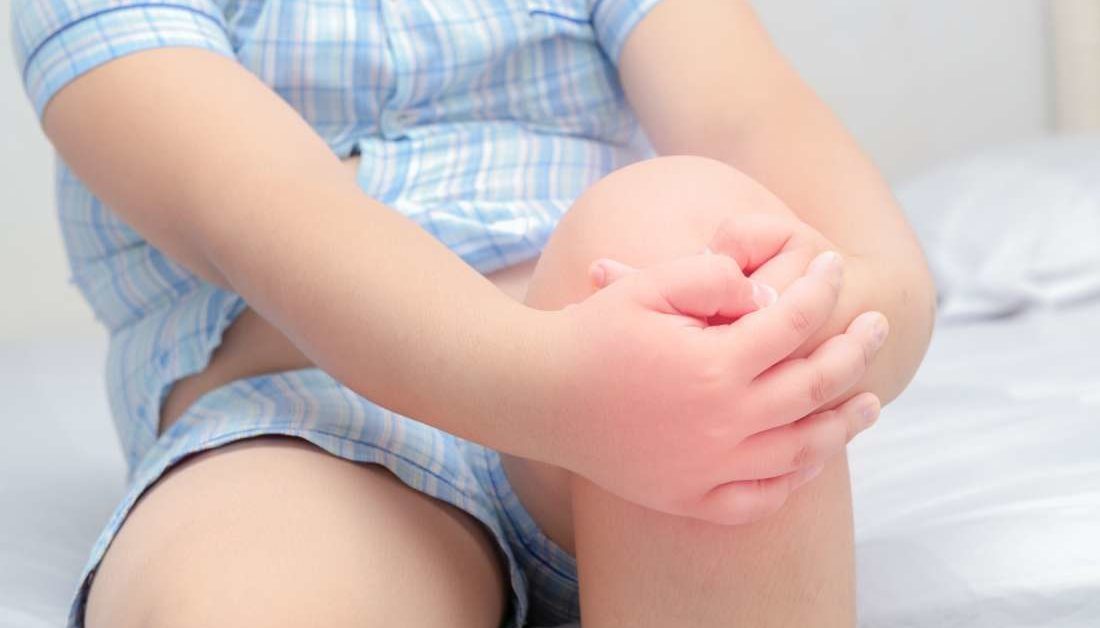

Joint pain in kids: Causes, treatment, and when to see a doctor

Foot Pain in the Bottom of the Foot | Stop Your Child's Foot Pain! | Fitting Children's Shoes

Pin on Foot & Ankle Conditions
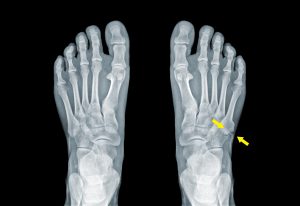
Kids Outer Foot Pain – My FootDr

What Causes Foot Pain in Toddler and What to Do? - New Kids Center

Foot and Leg Pain Centre » Babies & Children's Feet

Foot Health Facts for Children - Foot Health Facts

Top Pediatric Podiatrist in Houston |Severs Disease | Tanglewood Foot Specialists

Heel Pain: The Agony of De-Feet | Kids Fracture Care

Pain Relief For Very Sick Kids Is The Focus Of This Quick Response Team : Shots - Health News : NPR
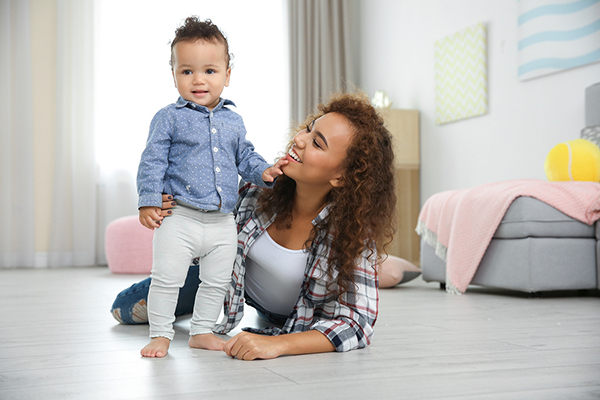

What Causes a Child to Limp?

Most Common Foot Problems in Children | Cornerstone Foot & Ankle
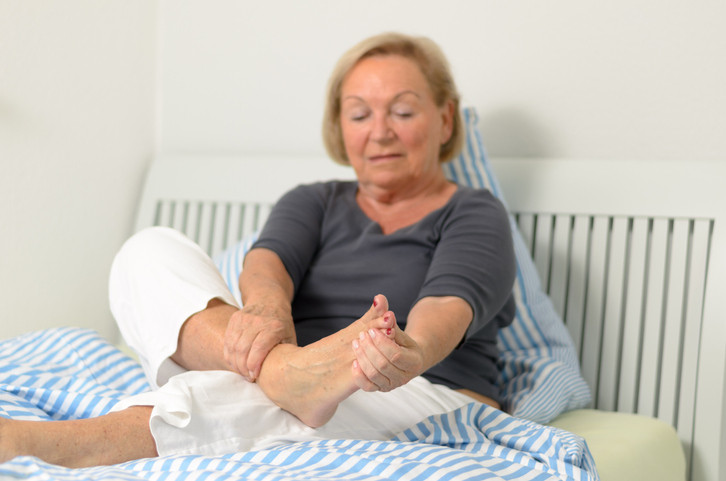

7 ways to fix foot pain - Harvard Health

Symptoms of Foot Damage and Common Foot Problems
Sever's Disease Can Be a Problem for Growing Kids — David Gleitman, DPM
Posting Komentar untuk "foot pain in kids"